Enzymes Catalyze Reactions Using Which of the Following Mechanisms
Three mechanisms that increase reaction in the active zone 1. Oxidoreductases are enzymes that transfer electrons from one place to another place and control oxidation activity.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action.
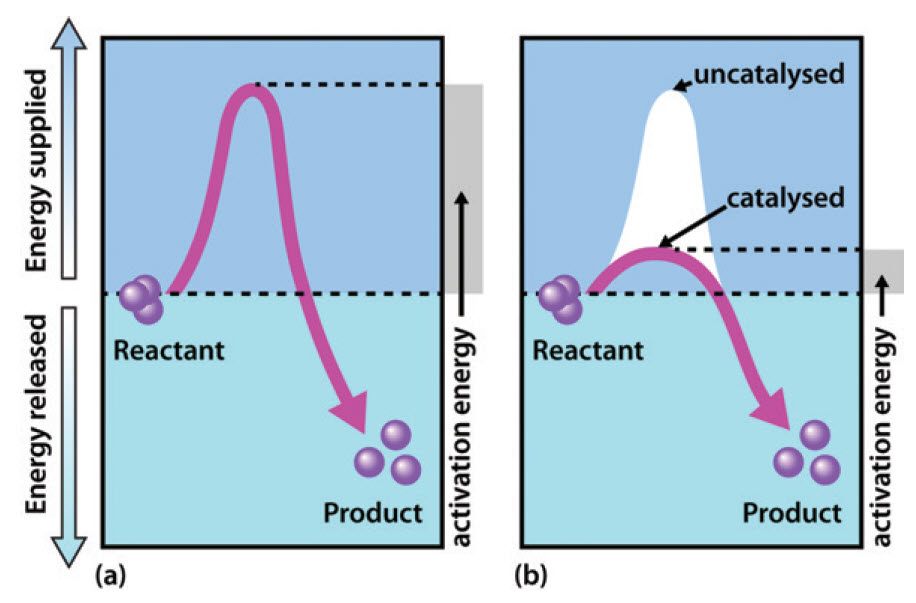
. Bringing two reactants close together. EnzymeE reactantS intermediate - 1ES intermediate - 1ES intermediate - 2EP intermediate - 2EP enzymeE productP This is known as the Michaelis - Menten mechanism. Enzymes which catalyze the chemical reactions that make life on the earth possible participate in the breakdown of nutrients to supply energy and chemical building blocks.
Enzymes consist of a number of cavities which are present on the outer surface. All of the above QUESTION 2 1 points Save Answer The enzymes in cells use the. Many enzymes utilize a concerted acid-base mechanism ie both acid and base catalysis.
Each type is specifically shaped to carry out one reaction. The assembly of those building blocks into proteins DNA membranes cells and tissues. They induce electronic strain in the substrate c.
The activity of the enzymes usually increases in the presence of a coenzyme or an activator such as Na Co2 The rate of the reaction increases due to the presence of a weak bond which exists between the enzyme and a metal ion. Enzymes speed up the biological reactions necessary for life. They bind preferentially to the transition state b.
Enzymes therefore allow scientists to control the exchange of atoms mechanically as explained by Science Daily. Bases catalyze the reaction by accepting a proton whereas acid by donating a proton. General acid-base catalysis - chymotrypsin.
The enzyme-catalyzed reactions involved in formation of the bicyclic clavam and carbapenem nuclei including β-amino acid and β-lactam formation have been reviewed and compared with those involved in penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis 05CC4251. Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis vary but are all similar in principle to other types of. By Staff Writer Last Updated March 31 2020 Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by first binding to molecules and then lining them up in ways that increase the probability of the molecules exchanging atoms when they collide.
These reactions typically involve Asp Glu His Cys Tyr and Lys residues. Principle mechanisms in enzyme catalyzed reactions. This division is based on the functional use of the enzymes.
2 Enzyme substrate complex ES converts to enzyme product EP complex E S E P This is slow step rate determining step 3 Enzyme product complex EP dissociates into enzyme E and. 1 Enzyme E binds to substrate S to form enzyme substrate complex ES E S E S This step is fast and reversible. Metal ion catalysis - carbonic anhydrase.
Enzymes are biological catalyst which increases the rate of the reaction without undergoing any change in itself. Mechanism of enzyme catalyst. The mechanism for enzyme catalysis includes following steps.
Enzymes can also break a larger substrate into two. In an enzyme-catalysed biochemical reaction the enzyme molecule binds specifically and reversibly to the substrate molecule resulting in formation and breaking of chemical bonds to produce the product. 100 T 80 60 3 40 20 0 0 1 0 PNPP concentration in mM Enzymes catalyze reactions using which of the following mechanisms.
Covalent catalysis leads to rapid progression of reactions by forming covalent bonds between enzyme and substrate. Catalysis by approximation - bring together substrates. The mechanism of enzyme action depends upon the two factors namely enzymes specificity and transition state of the reactants or substrates.
Altering the charge of. And the harnessing of energy to power cell motility neural function and muscle contraction. Leave a Comment Microbiology By Supriya N.
4 rows Ans. Protein phosphorylation plays a central role in controlling not only metabolic reactions but also many other cellular functions including cell growth and. Distort or strain the bonds making it more unstable and hence more reactive.
The synthesis of deuterium labelled l - and d-glutamate semialdehydes their evaluation as substrates for. Click hereto get an answer to your question A simple mechanism for enzyme - catalyzed reaction is given by the following set of equations. They bind to and orient substrates optimally d.
The enzymes specificity is due to its active site which seems like a small aperture or opening. Enzyme activity can be affected by temperature. Entrapment is an immobilization method that entraps enzyme in a confined space.
Thus there is formation of an unstable enzyme-substrate complex which immediately breaks into the product. Covalent catalysis - chymotrypsin. Enzymes are divided into oxidoreductases transferases hydrolases lyases isomerases and ligases.
The breakdown of glycogen is catalyzed by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase which is activated by phosphorylation in response to the binding of epinephrine to a receptor on the surface of the muscle cell.
Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms Of Enzymes Chemistry
Protein The Mechanism Of Enzymatic Action Britannica
No comments for "Enzymes Catalyze Reactions Using Which of the Following Mechanisms"
Post a Comment